Chapter 5: Working with models
Games typically don’t just use cubes and spheres. Instead, they use 3D models. In this chapter, we’ll learn how to load and use 3D models in Ambient.
Let’s download this free sample model from the official glTF sample repository.
Click the little download icon to the right to download it.
Next, create a folder named assets in your project, and add the file to that folder (see package structure).
Create a file called pipeline.toml in the assets folder, with the following content:
[[pipelines]]
type = "Models"
sources = ["*.glb"]
Note that this should not go in your ambient.toml. Pipelines are separate and are folder-specific.
In-depth: To learn more about how asset pipelines work, consult the reference documentation.
Finally, let’s use the model. In our server.rs, add the following lines:
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { Entity::new() .with_merge(Transformable { local_to_world: Default::default(), optional: TransformableOptional { scale: Some(Vec3::ONE * 0.3), ..Default::default() }, }) .with(model_from_url(), packages::this::assets::url("AntiqueCamera.glb")) .spawn(); }
This creates a new entity with the AntiqueCamera model. This model will be loaded in on the client.
You should now see something like this:
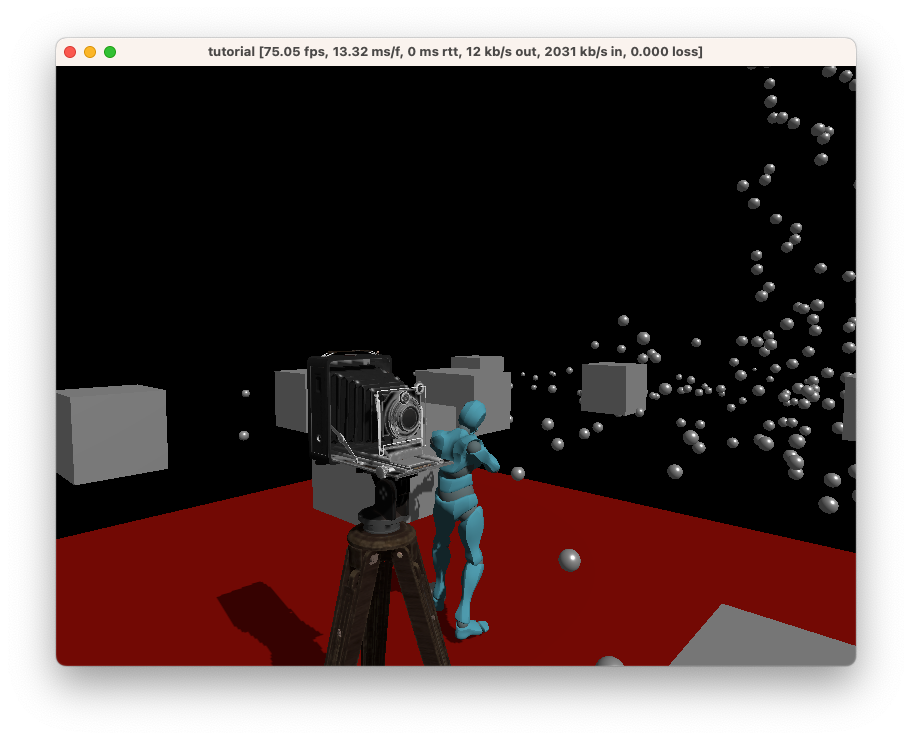
Great! We’ve learned how to load models into Ambient.
Tip: Use
prefab_from_urlinstead ofmodel_from_urlif you also want to include a collider.This instantiates a prefab for the model that includes a collider. However, note that the antique camera here does not have a collider and you will need to consider adding a collider through the primitive colliders or through another source.
See the physics example.
Source: The complete code for this chapter can be found here.